User Guide
About QuickContacts
QuickContacts is a contacts and schedule management system that enables you to track your contacts and manage your schedule with ease! As a busy individual with a considerable number of contacts and meetings to attend, you can seamlessly save contact and meeting information with QuickContacts. QuickContacts provides you with a bird’s eye view of all your meetings, making sure that you will never miss any of them again.
We, the developers at QuickContacts, understand the amount of time required to manage many contacts and maintaining a schedule with many meetings with them. Perfect for individuals that are looking for efficiency, QuickContacts can be used without having you to ever reach for your mouse. Complete with an autocomplete assistance, you can be assured that your time spent managing your contacts and schedule is minimised!
![]() Tip
Tip
For more details about QuickContacts’ features, you may head over to the Features section below!
QuickContacts is specially designed for:
- Seamless creation and management of contacts and meetings
- Users who have a large number of contacts and meetings
- Typists
This user guide provides a detailed documentation on QuickContacts and serves as an introduction on how to incorporate QuickContacts into your daily workflow. From having QuickContacts installed to making the best use out of QuickContacts, this user guide has everything you need. Head over to the Getting started section to get onboard!
Table of Contents
- About QuickContacts
- Table of Contents
- Using this User Guide
- Installation
- Quick Reference Guide
- Features
- Person-Related Commands
-
Meeting-Related Commands
- Adding a Meeting :
addm - Editing a Meeting :
editm - Sorting Meetings :
sortm - Finding Meetings by Attendee Name :
findm - View all Meetings :
findmwithout arguments - Export Meetings :
exportm - Import Meetings :
importm - Delete Meetings :
delm - Marking Meetings as done or undone :
markorunmark - Showing pending meetings :
pending
- Adding a Meeting :
- General Features
- FAQ
- Command summary
Using this User Guide
Welcome to QuickContacts!
If you have yet to install QuickContacts, head over to the Installation section to install QuickContacts.
Icon Coloured Boxes
Throughout this user guide, you may observe coloured boxes that provide useful information with an icon on its top-left indicating the type of information present.
![]() Tip
Tip
Tips empower you to make full use of QuickContacts.
![]() Note
Note
Notes are general information that gives you a better understand of QuickContacts.
![]() Caution
Caution
Cautions are warnings for you to note when using QuickContacts.
Installation
-
Ensure you have Java 11 or above installed in your computer
-
Download the latest version of
quickcontacts.jarfrom here -
Copy the file to an empty folder you want to use as the home folder for QuickContacts
-
Double-click on the downloaded
.jarfile to launch QuickContacts
And that’s it! You are good to go with QuickContacts.
![]() Tip
Tip
QuickContacts is packaged with sample contacts and meetings. To delete the default data, simply execute the clear
command.
![]() Caution
Caution
QuickContacts will generate default files in the same directory it is installed in on its first launch. Avoid
editing or deleting such files unless you know what you are doing!
Quick Reference Guide
This section will walk you through the essential parts of understanding and using QuickContacts in detail.
User Interface Layout
Upon launching QuickContacts, you will be greeted by the following Graphical User Interface (GUI).
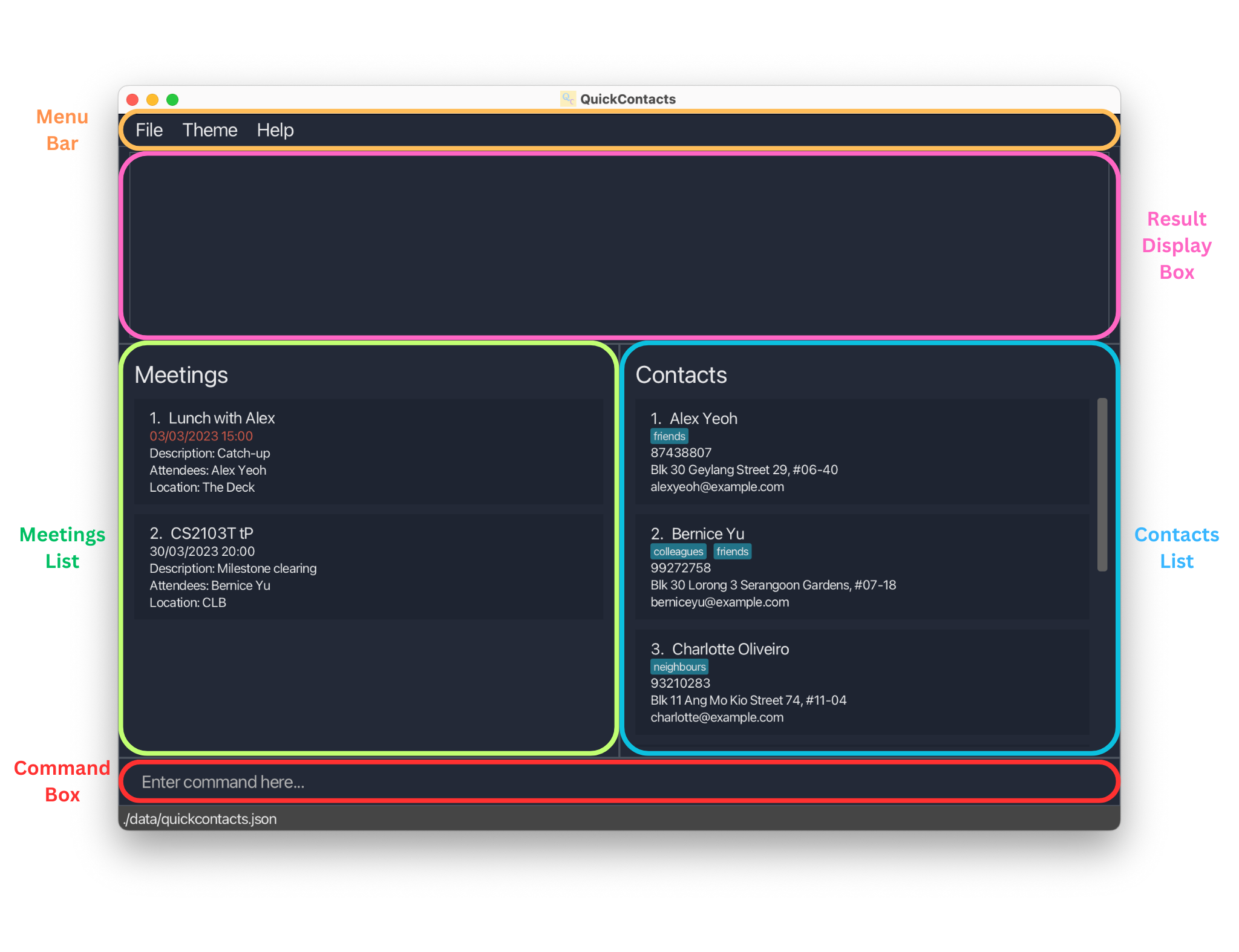
We can break the GUI into several parts:
- Menu Bar: This is where you find auxiliary features
- Result Display Box: This is where you get feedback from the command executed
- Meetings List: This is where you view all your meetings
- Contacts List: This is where you view all your contacts
- Command Box: This is where you input commands to interact with QuickContacts
Command Format
QuickContacts provides a powerful Command Line Interface (CLI) which rely heavily on commands. In this subsection, we will discover how the commands are designed.
Prefix
Prefixes are placeholders in a command that uniquely identify different input parameters. Each prefix is typically followed by the corresponding input data.
![]() Note
Note
- There are some input parameters that do not require any corresponding input data.
- There are some input data that share the same prefix. For example:
CONTACT_PHONE_NUMBERandMEETING_ATTENDEEshare the same prefixp/.
| Prefix | Corresponding Input Data |
|---|---|
a/ |
CONTACT_ADDRESS |
des/ |
MEETING_DESCRIPTION |
dt/ |
MEETING_DATE_TIME |
e/ |
CONTACT_EMAIL |
end/ |
MEETING_EXPORT_END_DATE |
f/ |
- |
l/ |
MEETING_LOCATION |
m/ |
MEETING_TITLE |
n/ |
CONTACT_NAME |
p/ |
CONTACT_PHONE_NUMBER or MEETING_ATTENDEE
|
start/ |
MEETING_EXPORT_START_DATE |
t/ |
CONTACT_TAG |
Understanding Commands
Now that we are familiar with the prefixes and corresponding input data, let us put them together and see how a command works. Take the following as an example:
Command: add n/CONTACT_NAME [p/CONTACT_PHONE_NUMBER] [e/CONTACT_EMAIL] [a/CONTACT_ADDRESS] [t/CONTACT_TAG]...
| Command Component | Component Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
add |
Command Keyword | Represents the action executed by QuickContacts |
n/, p/, e/, a/, t/
|
Prefix | Uniquely identifies the corresponding input data |
CONTACT_NAMECONTACT_PHONE_NUMBERCONTACT_EMAILCONTACT_ADDRESSCONTACT_TAG
|
Input Data | Placeholders for the actual data to be supplied for the command |
![]() Note
Note
-
[]means that the parameter is optional. -
...means that the parameter can be supplied multiple times in the same command input.
A valid executable command of this example form is:
add n/Noah t/friend t/nus t/cs2103t
The above command would create a new contact with the name Noah and tags friend, nus and cs2103t.
The phone number, email address and address of Noah will be left empty as they are not provided.
![]() Tip
Tip
Command prefixes can be specified in any order. For example: add t/friend t/nus n/Noah t/cs2103t is equivalent to our
example above.
![]() Note:
Note:
- If a parameter is expected only once in the command, but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of
the parameter will be taken.
e.g. if you specifyn/Noah n/Peter, onlyn/Peterwill be taken. - Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,list,exitandclear) will be ignored.
e.g.help 123will be interpreted ashelp.
Date and Time Formats
QuickContacts allow for various date and time formats to be inputted for commands that takes them in as arguments, for
example addm. Below, we can find the valid date and time formats.
![]() Tip
Tip
Date and time formats can be mixed and matched. For example, ddMMyyyy HHmm.
Date Formats
| Date Format | Example | Meaning | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ddMMyyyy | 01012023 | 1st January 2023 |
| 2 | dd-MM-yyyy | 01-01-2023 | 1st January 2023 |
| 3 | dd.MM.yyyy | 01.01.2023 | 1st January 2023 |
| 4 | dd/MM/yyyy | 01/01/2023 | 1st January 2023 |
| 5 | ddMM | 0101 | 1st January of the current year |
![]() Note:
Note:
-
ddrefers to the date represented with 2 digits (e.g.01for the first day of the month instead of1) -
MMrefers to the month represented with 2 digits (e.g.08for August instead of8) -
yyyyrefers to the year represented with 4 digits (e.g.2023instead of23)
![]() Tip
Tip
ddMM is a quick way to specify a date of the current year without needing the year. For example, specifying 0101
in year 2023 is the same as 01012023.
Time Formats
| Time Format | Example | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | HHmm | 0100 |
| 2 | HH:mm | 01:00 |
| 3 | HH.mm | 01.00 |
| 4 | hmma | 100AM |
| 5 | h:mma | 1:00AM |
| 5 | h.mma | 1.00AM |
![]() Note:
Note:
-
HHrefers to the hour in 24-hour time format represented with 2 digits (e.g.00for 12 midnight instead of1) -
hrefers to the hour in 12-hour time format represented with 1 or 2 digits (e.g.1for 1 o’clock,12for 12 o’clock) -
mmrefers to the minute represented with 2 digits (e.g.01for the first minute instead of1) -
arepresentsAMorPMfor 12-hour time format
Features
Here, you may find all the details about every feature that QuickContacts provide to empower you to make full use of the power of QuickContacts.
Autocomplete inputs
Simply hit the TAB key on your keyboard when you are entering a certain command to have QuickContacts autocomplete the
next nearest command word similar to the one you are typing!
Examples:
-
a->addafter hittingTAB(sinceaddis the next most similar command word) -
ex->exportafter hittingTAB
Autocompletion also works for the next possible prefix for a given command! This way, you will never have to memorise any prefix nor syntax for commands.
Examples:
-
add->add n/after hittingTAB(sincen/is the next prefix foradd) -
add n/Bobby->add n/Bobby p/after hittingTAB(sincep/is the next prefix foraddaftern/)
![]() Note:
Note:
- Autocomplete only works for command words and prefixes that expect a corresponding input data. You may refer to the Prefix section for more details on prefixes.
- If input matches a command, Autocomplete will autocomplete the prefixes for the command. If the command does not require any prefix, autocomplete will not do anything.
![]() Tip
Tip
Prefix autocomplete behaviour defers from commands to enhance user experience. For example:
-
edit 1 n/->edit 1 p/after hittingTAB(if you did not input anything for the prefixn/, it would be probable that you do not want to edit that field)
Traversing commands
Have you ever wanted to input commands similar to one that you have just inputted? With command traversal provided in QuickContacts, you will never have to copy and paste commands ever again.
All you have to do is to hit the UP and DOWN arrow keys on your keyboard to go to the previous and next command
respectively. It is as simple as that!
Person-Related Commands
In this subsection, you may find all the commands that are related to contacts.
Adding a person: add
Adds a person to the address book.
- The name of a person is case-sensitive, thus
John Doeandjohn doeare considered different persons.
Format: add n/CONTACT_NAME [p/CONTACT_PHONE_NUMBER] [e/CONTACT_EMAIL] [a/CONTACT_ADDRESS] [t/CONTACT_TAG]...
![]() Caution
Caution
Tags of more than 10 characters are unsupported! UI artifacts may occur.
Examples:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01add n/Betsy Crowe t/friend e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Prison p/1234567 t/criminal
Listing all persons : list
Shows a list of all persons in the address book.
Format: list
Editing a person : edit
Edits an existing person in the address book.
Format: edit INDEX [n/CONTACT_NAME] [p/CONTACT_PHONE_NUMBER] [e/CONTACT_EMAIL] [a/CONTACT_ADDRESS] [t/CONTACT_TAG]...
- Edits the person at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the person will be removed i.e adding of tags is not cumulative.
- You can remove all the person’s tags by typing
t/without specifying any tags after it.
Examples:
-
edit 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.comEdits the phone number and email address of the 1st person to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively. -
edit 2 n/Betsy Crower t/Edits the name of the 2nd person to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags.
Finding persons by name : find
Finds persons whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
hanswill matchHans - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Hans Bowill matchBo Hans - Only the name is searched.
- Only full words will be matched e.g.
Hanwill not matchHans - Persons matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.Hans Bowill returnHans Gruber,Bo Yang
Examples:
-
find JohnreturnsjohnandJohn Doe -
find alex davidreturnsAlex Yeoh,David Li
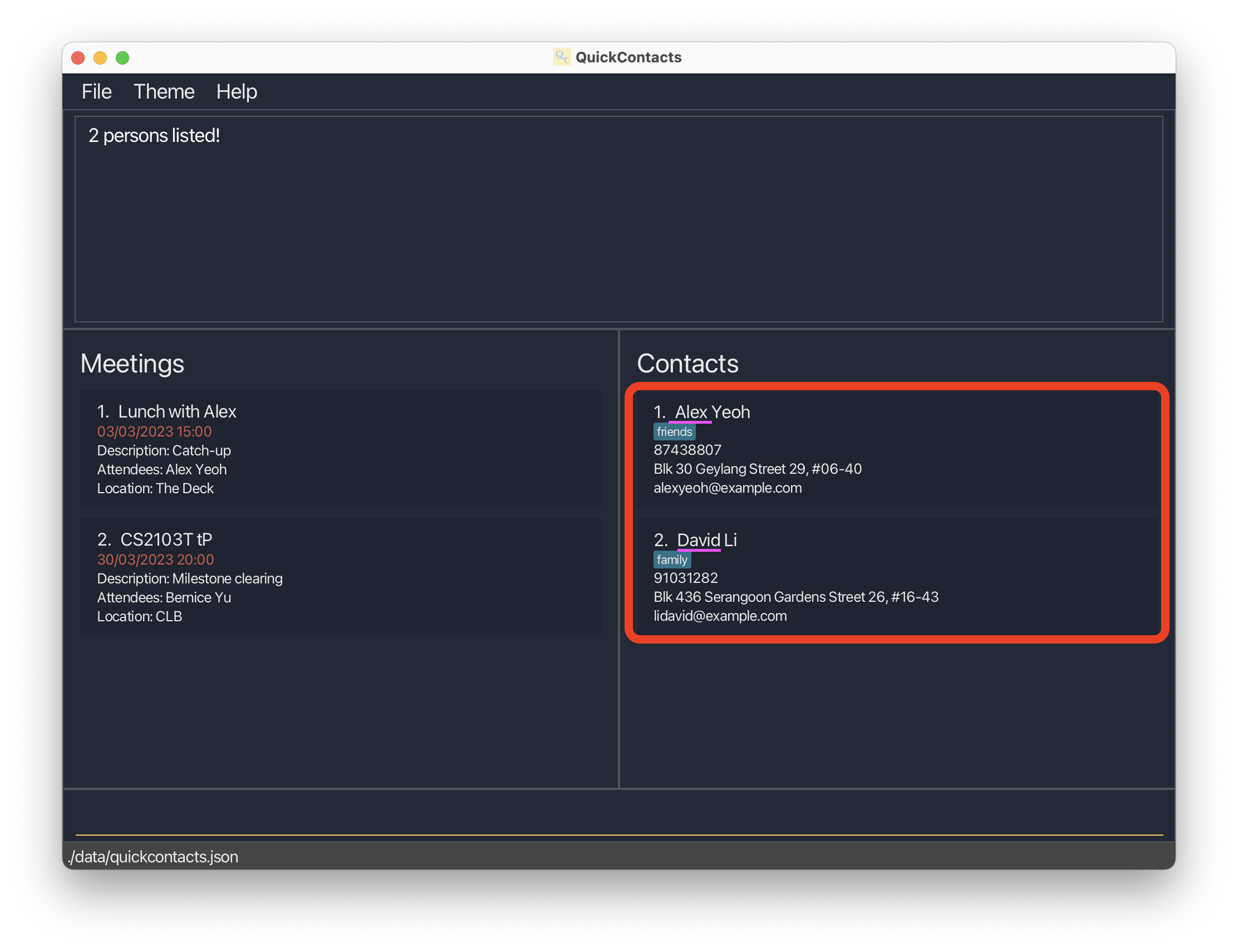
Deleting a person : delete
Deletes the specified person from the address book.
Format: delete INDEX
- Deletes the person at the specified
INDEX. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list.
- The index must be a positive integer: 1, 2, 3…
Examples:
-
listfollowed bydelete 2deletes the 2nd person in the address book. -
find Betsyfollowed bydelete 1deletes the 1st person in the results of thefindcommand.
Deleting a person does not affect any meetings that have already been created with the person as one of the attendees.
Exporting of contact : export
- Exports the persons at the specified
INDEXes. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list.
- The index must be a positive integer: 1, 2, 3…
Format: export p/INDEX [p/MORE_INDEXES]...
Importing of contacts : import
- Imports the persons in the provided JSON.
- The JSON must contain a valid array of persons
Example:
[
{
"name": "Alice Pauline",
"phone": "94351253",
"email": "alice@example.com",
"address": "123, Jurong West Ave 6, #08-111",
"tagged": [
"friends"
]
},
{
"name": "Benson Meier",
"phone": "98765432",
"email": "johnd@example.com",
"address": "311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25",
"tagged": [
"owesMoney",
"friends"
]
}
]
![]() Tip
Tip
You can append f/ to force import regardless of duplicate values.
![]() Note
Note
f/ will be your last argument, if added.
Duplicate values will still be ignored, but you can be assured the value is added if it did not exist before.
Format: import JSON [f/]
Meeting-Related Commands
In this subsection, you may find all the commands that are related to meetings.
Adding a Meeting : addm
Adds a meeting to the address book.
Format: addm m/MEETING_TITLE dt/MEETING_DATE_TIME [p/MEETING_ATTENDEE]... [l/MEETING_LOCATION] [des/MEETING_DESCRIPTION]
Constraints:
-
MEETING_DATE_TIMEmust be provided in the format as shown here. -
MEETING_ATTENDEEmust be a valid contact in the address book.
Examples:
addm m/CS2103T Tutorial p/John Doe p/Jane Doe dt/04-01-2023 10:00 l/COM1-B103 des/CS2103T Tutorialaddm m/CS2103T Tutorial p/John Doe p/Mary Jane dt/04-01-2023 22:22 l/COM1-B103 des/CS2101 Tutorial
Editing a Meeting : editm
Edits an existing meeting in the meeting book.
Format: editm INDEX [m/MEETING_TITLE] [p/MEETING_ATTENDEE]... [dt/MEETING_DATE_TIME] [l/MEETING_LOCATION] [des/MEETING_DESCRIPTION]
- Edits the meeting at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed meeting list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3,… - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
-
MEETING_DATE_TIMEmust be provided in the format as defined here.
Example:
-
editm 1 m/Project Update dt/04-01-2023 10:00Edits the date/time first meeting to be on04-01-2023 10:00, and changes its title toProject Update.
Sorting Meetings : sortm
Sorts meetings in the currently displayed address book by a specified attribute, in ascending order.
Format: sortm ATTRIBUTE [r]
- Sorts the meetings in the address book by the specified
ATTRIBUTE:
| Prefix | ATTRIBUTE |
|---|---|
m/ |
Meeting Title |
dt/ |
Date/Time |
l/ |
Location |
des/ |
Description |
- If the
roption is included, the meetings will be sorted in reverse(descending) order. - Meetings with the same value for the specified attribute will be sorted by date/time in ascending order.
- Examples:
-
sortm m/sorts meetings by title in ascending order. -
sortm dt/rsorts meetings by date/time in descending order.
-
![]() Note:
Note:
Autocomplete is not designed for attributes such as m/ for sortm as it is not a prefix that expects a corresponding
input data. For more details, refer to the autocomplete section.
Finding Meetings by Attendee Name : findm
Find meetings whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: findm KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
hanswill matchHans - Space is delimiter, so if you search
John Doeit will list all people with eitherJohnorDoein their name. - Only the name of attendees in meeting are searched
- Only full words will be matched e.g.
Hanwill not matchHans - Meetings matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.John Doewill return Meetings that contain eitherJohn Doe, orDoe John
Examples:
-
findm JohnreturnsMeetingthat containsattendeeswhose Name containsJohn -
findm John MaryreturnsMeetingthat containsattendeeswhose Name containsJohnorMary
View all Meetings : findm without arguments
Shows a list of all meetings in the meeting book.
Format: findm
- No parameters are required.
- If arguments are given, will instead behave like as stated here
Export Meetings : exportm
Exports the meetings at the specified INDEX’s and between start and end dates.
- If only
MEETING_EXPORT_START_DATEprovided, meetings afterMEETING_EXPORT_START_DATE, inclusive, will be exported - If only
MEETING_EXPORT_END_DATEis provided, meetings afterMEETING_EXPORT_END_DATE, inclusive, will be exported - If both are provided, meetings between the two dates, inclusive, will be exported
- Regardless of the above, meetings at provided INDEXes will be provided
- At least one of the parameters must be provided
- The indexes refer to the index numbers shown in the displayed meetings list
- The indexes must be positive integers 1, 2, 3…
- The start and end dates must be valid dates in the format as defined here.
Format: exportm m/INDEX [p/MORE_INDEXES]... [start/MEETING_EXPORT_START_DATE] [end/MEETING_EXPORT_END_DATE]
Example: exportm start/01/01/23 m/1 will export the first meeting and any meetings starting from 01/01/23
Import Meetings : importm
- Imports the meetings in the provided JSON.
- The JSON must contain a valid array of meetings
Example:
[
{
"title": "Dinner with Alice",
"dateTime": "01/02/2023 19:00",
"attendees": [
{
"name": "Alice Pauline",
"phone": "94351253",
"email": "alice@example.com",
"address": "123, Jurong West Ave 6, #08-111",
"tagged": [
"friends"
]
}
],
"location": "NUS",
"description": "Weekly catchup"
},
{
"title": "Zoom meeting for agenda planning",
"dateTime": "13/03/2023 12:45",
"attendees": [
{
"name": "Alice Pauline",
"phone": "94351253",
"email": "alice@example.com",
"address": "123, Jurong West Ave 6, #08-111",
"tagged": [
"friends"
]
}
],
"location": "https://us02web.zoom.us/j/999?pwd=ABCdEfGmNopQrSt12",
"description": "Plan for project work"
}
]
Optional Parameter f/ that forces imports regardless of duplicate values. f/ does not take any values.
Format: importm JSON f/
Delete Meetings : delm
Deletes the specified meeting.
Format: delm INDEX
- Deletes the meeting at the specified
INDEX. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed meetings list.
- The index must be a positive integer: 1, 2, 3…
Examples:
-
findmfollowed bydelm 2deletes the 2nd meeting.
Marking Meetings as done or undone : mark or unmark
Marks the specified meetings as either done or undone.
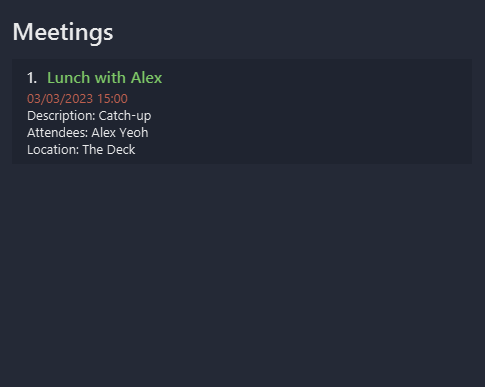
Format: mark m/INDEX [m/INDEXES]... or unmark m/INDEX [m/INDEXES]...
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed meetings list.
- The index must be a positive integer: 1, 2, 3…
![]() Note
Note
Meetings marked as done will have green colored titles.
Showing pending meetings : pending
![]() Tip
Tip
To view all meetings, use findm with no parameters.
Shows meetings that are not marked as done and those that are in the future i.e not over yet.
Format: pending
General Features
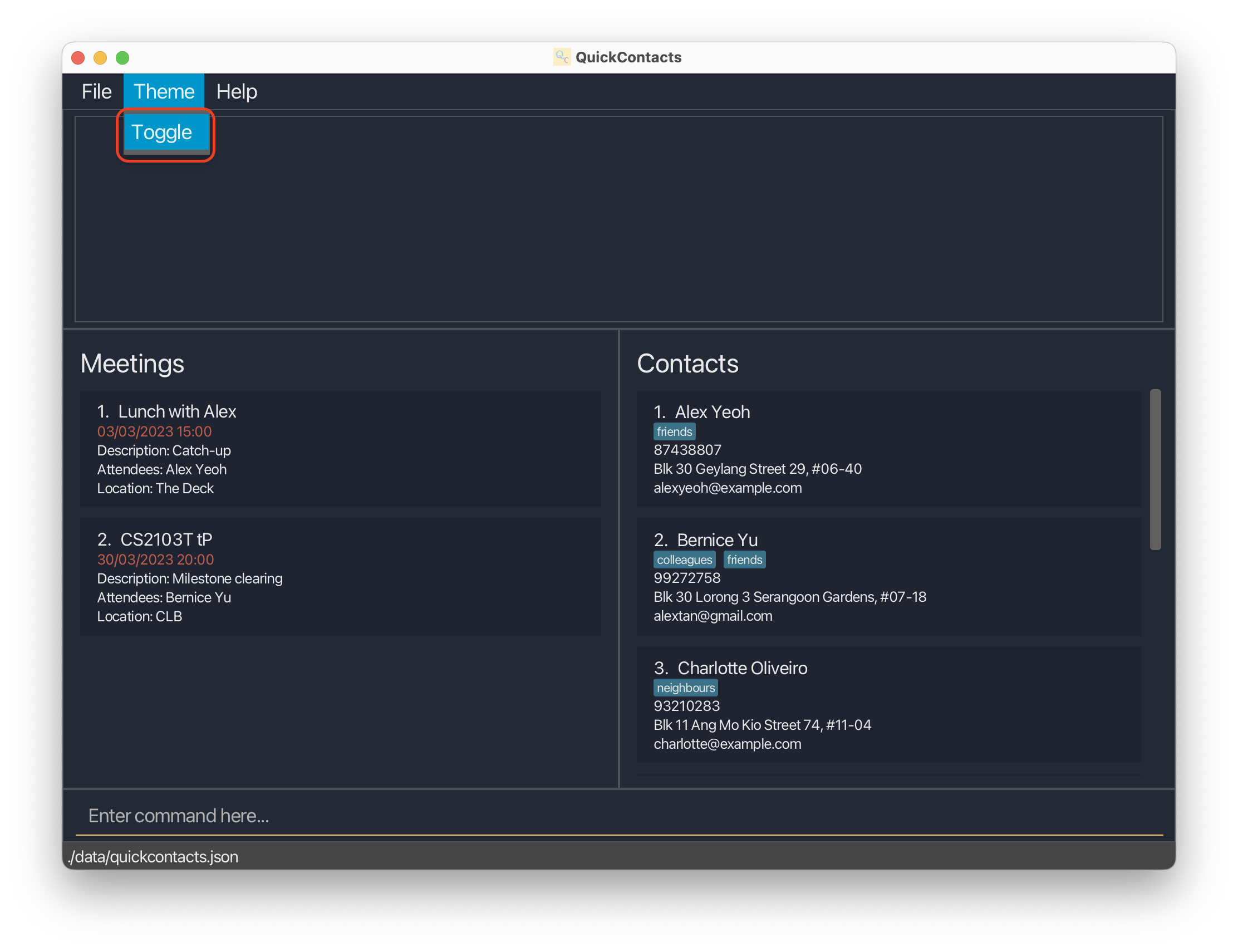
Theme toggling
Toggles the theme from dark to light or vice versa.
Viewing help : help
Shows a message explaining how to access the help page.
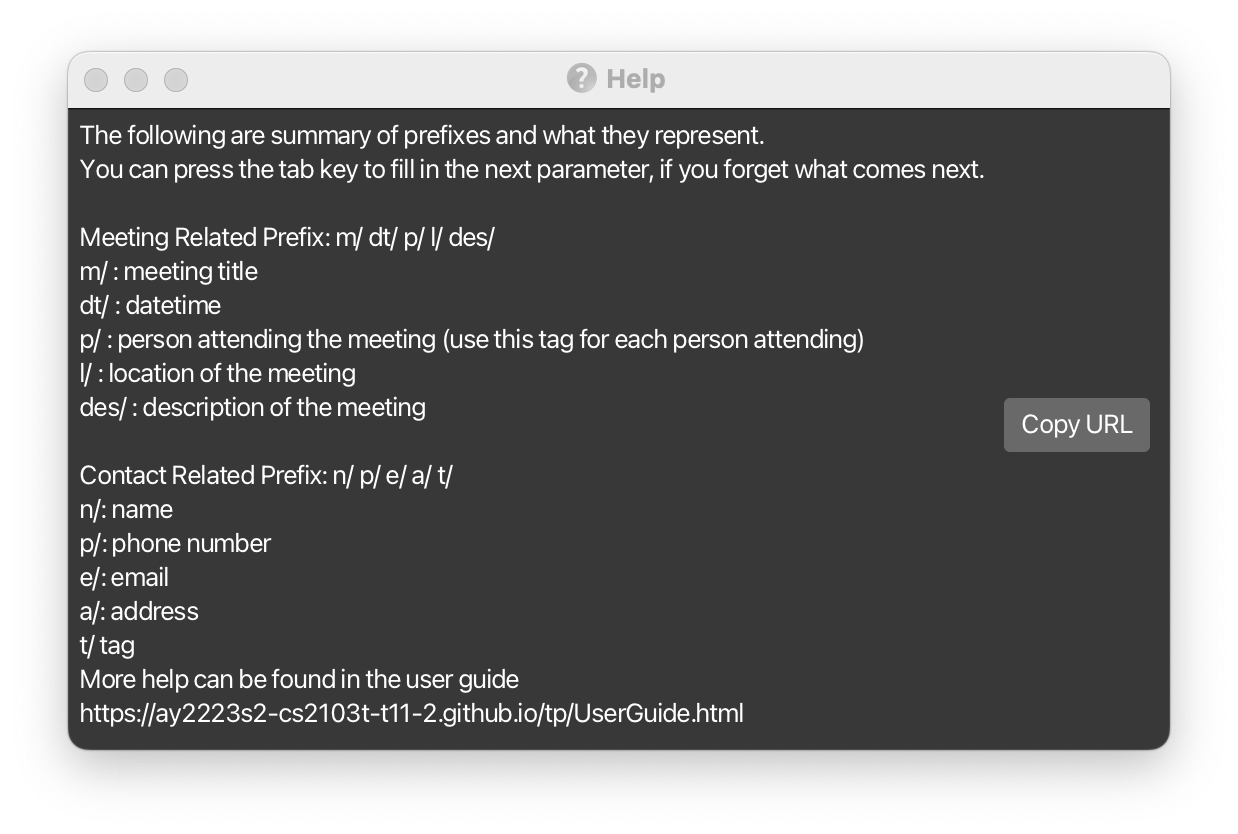
If used with a command word, shows a message explaining how to use the command in the output box.
Examples:
-
help addshows a message explaining how to use theaddcommand. -
help delmshows a message explaining how to use thedelmcommand.
Format: help [COMMAND_WORD]
Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries from the address book.
Format: clear
Saving the data
QuickContacts data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
QuickContacts data are saved as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/quickcontacts.json. Advanced users are welcome to
update data directly by editing that data file.
Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains
the data of your previous QuickContacts home folder.
Command summary
Person Commands
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Create a contact |
add n/CONTACT_NAME [p/CONTACT_PHONE_NUMBER] [e/CONTACT_EMAIL] [a/CONTACT_ADDRESS] [t/CONTACT_TAG]... e.g., add n/James Ho p/22224444 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 t/friend t/colleague
|
| List all contacts | list |
| Edit a contact |
edit INDEX [n/CONTACT_NAME] [p/CONTACT_PHONE_NUMBER] [e/CONTACT_EMAIL] [a/CONTACT_ADDRESS] [t/CONTACT_TAG]...e.g., edit 2 n/James Lee e/jameslee@example.com
|
| Find a contact |
find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., find James Jake
|
| Delete a contact |
delete INDEXe.g., delete 3
|
| Export a contact |
export p/INDEX [p/MORE_INDEXES]... e.g., export p/1 p/2 p/3
|
| Import a contact | import VALID_JSON |
Meeting Commands
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Create a meeting | addm m/MEETING_TITLE dt/MEETING_DATE_TIME [p/MEETING_ATTENDEE]... [l/MEETING_LOCATION] [des/MEETING_DESCRIPTION] |
| Edit a meeting | editm INDEX [m/MEETING_TITLE] [dt/MEETING_DATE_TIME] [p/MEETING_ATTENDEE]... [l/MEETING_LOCATION] [des/MEETING_DESCRIPTION] |
| Sort meetings |
sortm SORT_FIELD [r] e.g., sortm dt/
|
| Find a meeting |
findm KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] e.g, findm James Jake
|
| List all meetings | findm |
| Export a meeting |
exportm m/INDEX [m/MORE_INDEXES]... [start/MEETING_EXPORT_START_DATE] [end/MEETING_EXPORT_END_DATE] e.g., exportm m/1 m/2 m/3
|
| Import a meeting | importm VALID_JSON |
| Delete a meeting |
delm INDEX e.g., delm 3
|
| Mark meeting as done | mark m/INDEX [m/MORE_INDEXES]... |
| Mark meeting as not done | unmark m/INDEX [m/MORE_INDEXES]... |
| View pending Meetings | pending |
General Commands
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Help | help [COMMAND_WORD] |
| Reset all data | clear |
| Exit the app | exit |